——以“钻石收集者”与“Subsequence”为例
如果有同学细心去做Codeforces,会发现有这么一类标签叫Two Pointers。没错,这就是我们今天的主角——尺取法。
还有一部分同学会将尺取法叫成毛毛虫法。
其实这是相当形象的一种叫法,我们可以通过这个示例来非常直观的了解这个算法
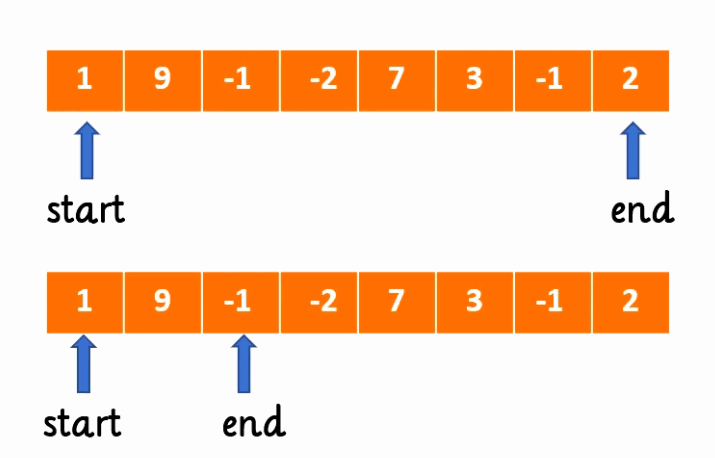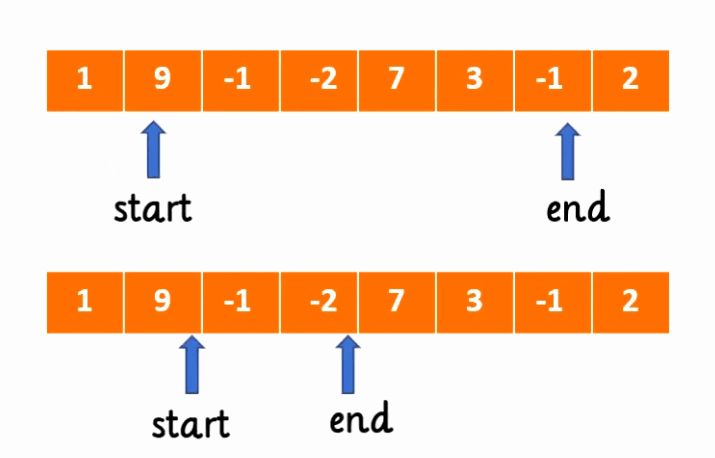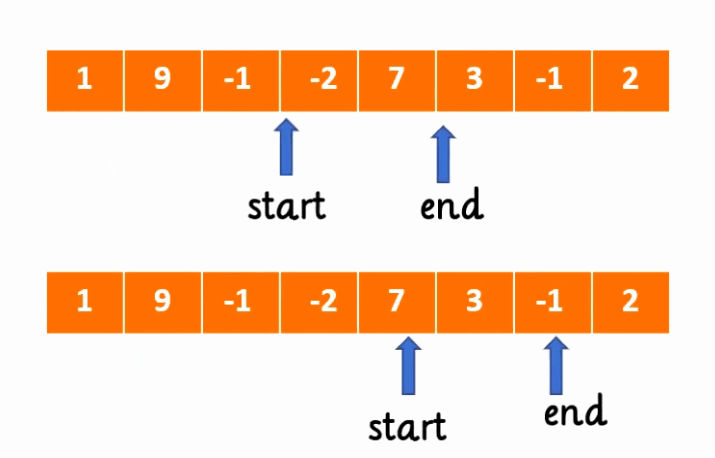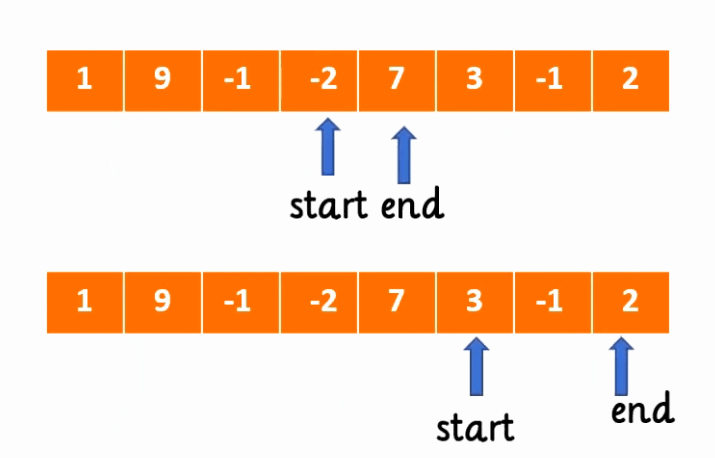
我们可以看到有一个start标签与end标签,这两个指针分别指向了数组中的两处,而这两个指针之间划定了一个连续区间,也就非常便于我们解决一些连续区间最大最小的问题。
不妨先看这样的一个示例
Description
总是喜欢亮闪闪的东西的奶牛Bessie空闲时有挖掘钻石的爱好。她收集了\(N\)颗不同大小的钻石并且她希望将其中一些钻石放在谷仓展览室的一个盒子里。由于Bessie希望盒子里面的钻石在大小上相对接近,她不会将大小相差大于K的钻石放在盒子里。 现在给出\(K\),请帮助Bessie计算她最多能选出多少颗钻石放在盒子里面。
Input
单组输入。
第一行2个正整数\(N\)和\(K\),之间用一个空格隔开 \((1<=N<=1e6,0<=K<=1e5)\) 接下来的\(N\)行,每行包括1个正\(S_i\),表示第i颗钻石的大小\((0<=S_i<=1e5)\)
Output
一行一个整数,表示Bessie最多能选出多少颗钻石在盒子里面展览。
Analysis
这一题我们就是一种优雅的暴力,既然要求钻石之间的大小相差不能超过\(K\),那也就是要求一堆钻石当中最大的应该要小于等于最小的加\(K\),这里利用尺取法可以非常便捷的解决这个问题。
因为确定起点以后最佳的终点必然就得到了确定,就是选取小于等于\(a[i]+k\)中最大的哪一个,而这而这个终点又可以利用upper_bound()去处理,非常好操作
Accepted Code
/*
* @Author: Gehrychiang
* @Date: 2020-02-18 20:04:01
* @Website: www.yilantingfeng.site
* @E-mail: gehrychiang@aliyun.com
*/
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxm = 1e6 + 5;
int a[maxm];
int main()
{
int n, k;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
stable_sort(a, a + n); //排序
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int l = i;
int r = upper_bound(a, a + n, a[i] + k) - a - 1; //得到最优的右端
ans = max(ans, r - l + 1);
}
cout << ans << endl;
return 0;
}
接下来的这一题稍微复杂一些
Description
给定长度\(N (10 < N < 100000)\) 的整数数列,以及整数 \(S (S < 100 000 000)\) ,求出总和不小于\(S\)的连续子序列的长度的最小值。
Input
第一行输入\(N\)和\(S\),第二行输入\(N\)个正整数。
Output
输出到满足要求的连续子序列的最小长度
如果没有则输出0。
Analysis
这一题的思路也是比较显然的,从起点和长度两方面即可确定下来一个尺的长度,暴力遍历即可。
如果是单纯按照尺的长度这么遍历非常有可能超时(事实上我就超时了)。那我们就应该将尺取法这个工具与其他的结合起来。
在这一题当中我的答案是在一个确定区间内的\([1,n]\)。
没错我们可以通过二分法来减少许多无谓的遍历,利用二分答案,我们去获取在某一个尺取长度下我所能够得到的最大的子序列和,将这个子序列和去和\(S\)比较,如果相比 \(S\) 大于等于他,说明这样的一个尺取长度一定大于等于最终的答案长度,如果小于,则说明这样的一个尺取长度一定小于最终的答案长度。将尺取法写在二分的chk函数内即可实现。
而事实也证明了二分法的确具有较高的时间优势。
一般的暴力解法需要500-800ms才能完成,而使用二分优化只需要70-90ms即可
Accepted Code
/*
* @Author: Gehrychiang
* @Date: 2020-02-19 12:12:30
* @Website: www.yilantingfeng.site
* @E-mail: gehrychiang@aliyun.com
*/
#include <*****>
using namespace std;
int a[100005];
long long n, s;
bool chk(int val) //得到在这个尺取长度下的最大的子序列和用来逼近我的答案长度
{
long long fir = 0;
long long maxer = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < val; j++) //首先获取最前端尺的和
{
fir += a[j];
}
maxer = max(maxer, fir);
for (int j = 1; j <= n - val; j++)
{
fir -= a[j - 1]; //减掉最前端的
fir += a[j + val - 1]; //加上最后一个
maxer = max(maxer, fir);
}
if (maxer >= s)
{
return true; //有点大了
}
else
{
return false; //有点小了
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
int flag = 0;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &s);
memset(a, 0, n);
long long tol = 0; //预先求和判断无解
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
tol += a[i];
if (a[i] >= s)
{
flag = 1;
}
}
if (flag)
{
cout << 1 << endl;
continue;
}
if (tol < s)
{
cout << 0 << endl;
continue;
}
//二分答案
int l = 2, r = n;
int mid;
int ans;
while (l <= r)
{
mid = (l + r) / 2;
if (chk(mid)) //里面包含了等于的情况
{
ans = mid;
r = mid - 1;
}
else
{
l = mid + 1;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}


前排,来一个第二题简短的代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const int maxn = 1e5 + 5;
int ans = 0x3f3f3f;
int sum[maxn], num[maxn];
int main()
{
int t;
while (~scanf(“%d”, &t))
{
while (t–)
{
int n, s;
memset(num, 0, sizeof(num));
memset(sum, 0, sizeof(sum));
scanf(“%d%d”, &n, &s);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
sum[i] = sum[i – 1] + num[i]; //前缀和
}
int ans = 0x3f3f3f;
bool flag = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 2; i <= n && j = s)
{
ans = min(ans, j – i);
++i;
flag = 1;
}
else
++j;
}
if (flag)
printf(“%d\n”, ans);
else
printf(“0\n”);
}
}
return 0;
}
希望更丰富的展现?使用markdown
望丰展?
Markdown